How to make web pages accessible
Links and link text
Use descriptive and meaningful link text so people know where a link will take them.
On this page
What links and link text do
Links in on webpages are usually a different colour and underlined. They work best when written as descriptive and meaningful text.
This helps all people, especially screen reader users because they can quickly skip through a list of links instead of reading a whole document.
Let people know what a link will do
Let people know what will happen or where they will go when selecting a link. Make it clear if a link goes to:
- content from an outside source, like (GOV.UK)
- a system that's different to a standard web page, like [Microsoft Forms]
- a different content format, like a [PDF] or other document file
- non-text content, like a [YouTube] video or [SoundCloud] audio podcast
- content with barriers to access, like [requires a login]
- an email address which can open an application the user does not want to use
You may have to restructure or reword content which contains links to better meet these recommendations.
Learn more about how to write good link text
Add and format links
How you add different links will depend on the website editing tool you're using.
On our website, content authors typically use a formatting toolbar 'link' icon to insert or edit:
- internal links by selecting a page from the 'Link to page' or 'Link to media' link pickers
- external links by pasting the full URL from a website
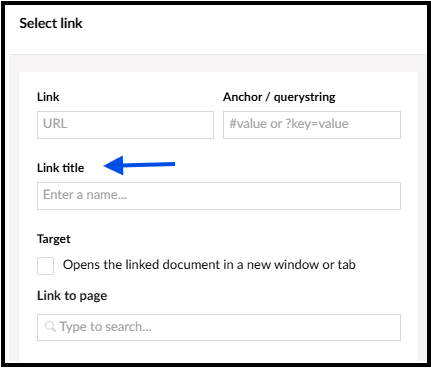
Link title (title text, screen tips, 'hover over' text)
The 'link title' found on many website editing tools is a message box that pop-ups when you move your mouse over a link or use a keyboard to move through links.
It's also known as title text, screen tips or 'hover over' text.
Link text that is already clear about where it goes does not need extra information added to the link title.
Using an unnecessary link titles could even hurt accessibility because:
- Desktop users might not know it's there, find it useful and the pop-up box may block visible content.
- Mobile users typically do not see it - if you hide important text in a link title, you exclude these users entirely.
- Screen reader users cannot hear them if links are listed and may find an added 'screen tip' confusing when reading through content.
Avoid using the 'link title' in most cases. Remove unnecessary link titles where possible (see screenshot).
Opening links in a new tab or window
Do not open most links in a new tab or window. This is because:
- users expect pages to open in the same window so they can use the back button easily
- it's easier for users who are not good with technology - they might not know how to switch between browser tabs on mobile devices
- fewer tabs means less confusion and visual clutter
- it's easier for people using screen readers
Some external links should open in a new tab or window. For example, if an external link is:
- to an online form or survey
- a secure website where personal information is submitted
This stops people from losing information they type in if they use the back button to go to a previous page.
Give the user advance warning, within the link text, if you open in a new tab. For example, 'Apply for a care needs assessment [opens in new tab]'
Related links
Some websites have related links or buttons located outside the main body content that allow users to navigate to related pages or topics.
Avoid linking to untrustworthy sites or to sites where a user must pay or register to access information.
When adding related links:
- consider them carefully, generally limit them to only the most important pages related to your content
- order them consistently across related pages of a similar level
- do not use directional language to refer to them because they can move on smaller screens, like ‘Go to the related links to the right of the screen.’
Check links and link text
Before you publish a web page with links, make sure all your links are descriptive and meaningful.
For examples of good and bad link text, go to our page on writing accessible links in content.
Then check:
- for unclear link text you may have missed, like "click here'
- that text in a button link performs an action
- that links work and take you to a new page or place
- PDFs or other files have their file types included within the link text in square brackets, like [PDF] or [YouTube]
- it's clear where external links take you, like 'Guidance on writing links (GOV.UK)'
- for unnecessary 'link titles' and remove them
Other checks to make
After you publish your web page, check you set up your links correctly.
- Open the web page in a web browser, like Microsoft Edge.
- Open WAVE Evaluation Tool (Microsoft Edge Addons)
- Go to the 'Details' panel to check for alerts and errors
- Check for and fix the following:
-
-
Errors: Empty link or a link that contains no text (Fix: Remove the empty link).
- Alert: Redundant link or adjacent links that go to the same URL (Fix: See if link text can be combined into a single link).
- Alert: Redundant title text or title attribute text is the same as link text (Fix: remove title text if possible).
- Alert: Underlined text (Fix: Remove underlining from text that's not a link - underlining should be reserved for link text).
-
Related resources
Guidance on writing links
- How to write hyperlink text for better web accessibility (Scope for business)
- Links and Hypertext - Introduction to Links and Hypertext (WebAIM)








